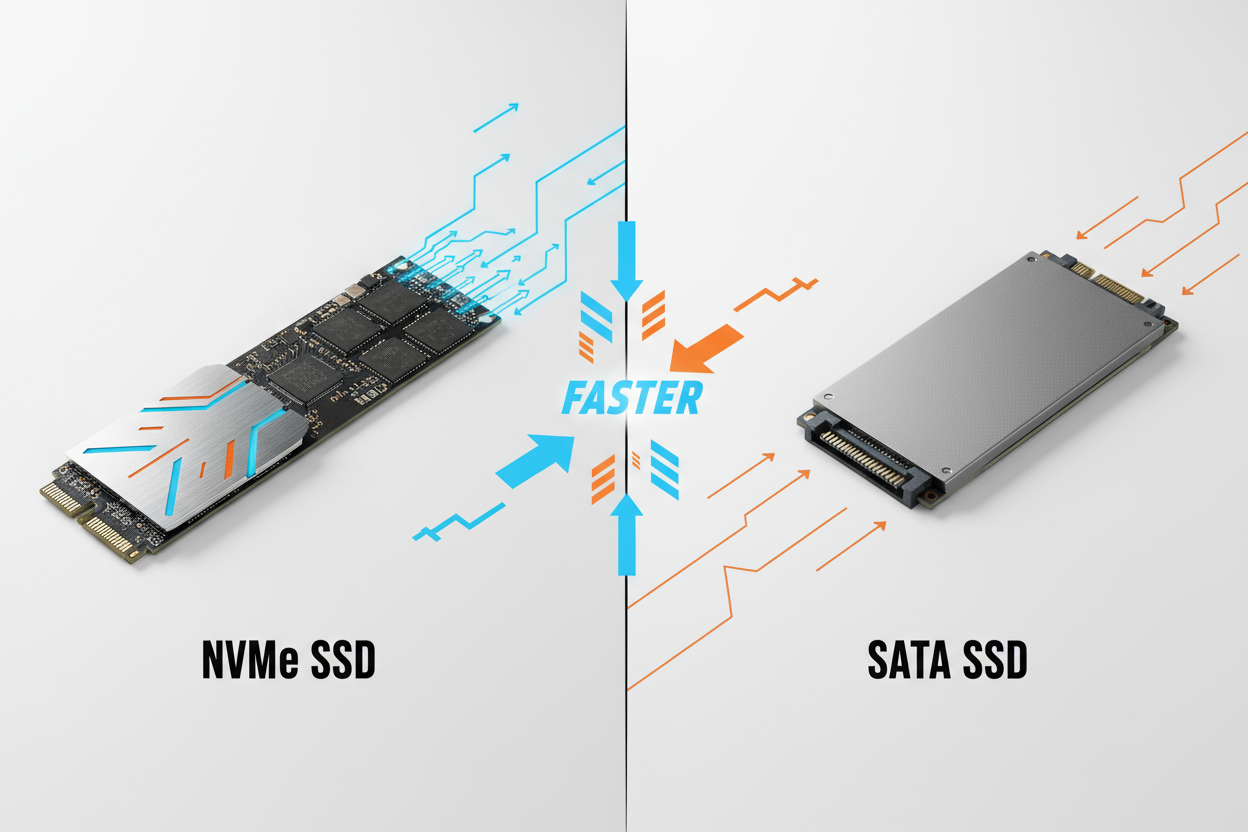
Es gab eine Zeit klobiger Festplatten, dann kamen die SSDs. Wer schon einmal einen PC zusammengebaut oder seinen Laptop aufgerüstet hat, kennt wahrscheinlich NVMe- und SATA-SSDs. Beide sind Solid-State-Drives und arbeiten deutlich leistungsfähiger als herkömmliche Festplatten.
Vergleicht man NVMe-SSDs mit SATA-SSDs, zeigt sich ein deutlicher Unterschied in Geschwindigkeit und Zukunftssicherheit. Aiffro hilft Ihnen dabei, NVMe-SSDs umfassend mit SATA-SSDs und NVMe-SSDs im Allgemeinen zu vergleichen.
Wir erklären Ihnen die Unterschiede und zeigen Ihnen, warum NVMe-SSDs für die meisten Anwender die bessere Wahl sind. Außerdem stellen wir Ihnen einige Beispiele aus der Praxis vor, die veranschaulichen, wie NVMe-Laufwerke für schnellen und zuverlässigen Speicher eingesetzt werden können.
Was ist eine SSD und warum hat sie HDDs ersetzt?
Bevor wir den Unterschied zwischen NVMe und SATA verstehen, müssen wir uns zunächst SSDs im Allgemeinen ansehen. Eine SSD (Solid State Drive) speichert Daten auf einem NAND-Flash-Speicherchip.
SSDs unterscheiden sich von Festplatten, die auf rotierenden Platten und einem beweglichen Lese-/Schreibkopf basieren, dadurch, dass sie keine beweglichen Teile besitzen. Diese Eigenschaften machen sie:
- Zuverlässiger und stoßfester.
- Effizienter beim Lesen und Schreiben von Daten.
- Weniger Lärm und kühler.
- Langlebiger.
- Energiesparmodus.
Diese Vorteile machen SSDs in den meisten modernen Laptops und Desktop-PCs zu einer besseren primären Speicheroption als HDDs. Doch auch bei SSDs muss die Schnittstelle mit dem Computer verbunden werden, was einen großen Unterschied in der Leistung ausmacht. An diesem Punkt kommen SATA-SSDs und NVMe-SSDs, die portablen SSDs, ins Spiel .
SATA-SSD: Die traditionelle Option
SATA-SSDs waren die ersten SSDs, die sich durchsetzten. Sie werden über dieselbe SATA-III-Schnittstelle angeschlossen, die ursprünglich für Festplatten entwickelt wurde. Diese Eigenschaft sorgt für hohe Kompatibilität, schränkt aber gleichzeitig ihre Leistung ein. Zu ihren wichtigsten Merkmalen gehören:
Höchstgeschwindigkeit:
Die maximale Geschwindigkeit liegt bei sequenziellen Lese- und Schreibvorgängen bei etwa 500–550 MB/s.
Formfaktor:
Üblicherweise haben diese Laufwerke eine Größe von 2,5 Zoll. Einige neuere Geräte verwenden jedoch M.2-Laufwerke, die kleiner und kompakter sind.
|
Vorteile |
Nachteile |
|
Erschwinglich |
Deutlich langsamer als NVMe |
|
Arbeiten mit älteren Systemen |
Beschränkt durch den alten SATA-Standard |
|
Zuverlässig |
Für alle, die von einer HDD umsteigen, fühlt sich eine SATA-SSD wie ein enormer Geschwindigkeitssprung an. Der Unterschied wird aber deutlich, wenn man sie mit NVMe vergleicht.
NVMe SSD: Entwickelt für Höchstgeschwindigkeit
Non-Volatile Memory Express oder NVMe ist ein neueres Speicherprotokoll, das speziell für SSDs entwickelt wurde. Es nutzt PCI-Express-Lanes (PCIe) anstelle der älteren SATA-Verbindung.
Es ermöglicht die direkte Kommunikation des Laufwerks mit der CPU. Diese Konfiguration beseitigt die Einschränkungen der vorherigen Geräte und ermöglicht deutlich höhere Geschwindigkeiten:
Typische Geschwindigkeiten:
Es bietet Geschwindigkeiten von 2000 MB/s bis 3500 MB/s auf PCIe 3.0-Laufwerken. Die PCIe 4.0-Modelle erreichen 7000 MB/s, und PCIe 5.0 verspricht noch mehr.
Latenz:
Das Vorgängermodell bot eine geringe Reaktionszeit beim Öffnen von Apps, Laden von Dateien oder Multitasking. Die NVMe-SSD sorgt für eine schnelle und effiziente Reaktion.
Formfaktor:
Die meisten NVMe-SSDs nutzen den M.2-Steckplatz auf dem Mainboard. Wir bieten aber auch externe Versionen in tragbaren Gehäusen an.
NVMe-SSDs bieten einen spürbaren Geschwindigkeits- und Reaktionsfähigkeitsschub für Spiele, Videobearbeitung oder die Verarbeitung großer, datenintensiver Aufgaben.
Hauptunterschiede zwischen NVMe- und SATA-SSDs
Hier ist ein Vergleich von NVMe- und SATA-SSDs, um deren Eigenschaften besser zu verstehen.
|
Besonderheit |
SATA SSD |
NVMe SSD |
|
Schnittstelle |
SATA III (6 Gbit/s) |
PCIe (x4, x8) mit NVMe-Protokoll |
|
Höchstgeschwindigkeit |
~550 MB/s |
2000–7000+ MB/s |
|
Latenz |
Höher |
Untere |
|
Formfaktor |
2,5 Zoll oder M.2 |
Meistens M.2, U.2 oder portable NVMe |
|
Preis |
Günstiger |
Etwas teurer |
Die Zahlen sprechen für sich: NVMe-SSDs sind in puncto Geschwindigkeit fünf- bis zehnmal schneller als SATA-SSDs.
Leistung in der Praxis
Benchmarks deuten darauf hin, dass NVMe-SSDs deutlich schneller sind als SATA-SSDs, aber lassen Sie uns einen praktischen Vergleich durchführen, um die tatsächliche Leistung zu überprüfen:
Bootzeiten
- Die Bootzeit eines Systems mit einer NVMe-SSD ist etwas besser als die einer SATA-SSD, die zwar schnell, aber nicht so blitzschnell ist.
App- und Spielladung
- Systeme mit NVMe-SSDs verkürzen die Ladezeiten in modernen Spielen drastisch und beschleunigen große Anwendungen wie Photoshop oder Premiere Pro.
Dateiübertragungen
- NVMe-SSDs eignen sich gut für die Dateiübertragung, da sie ein 50 GB großes Videoprojekt in Sekundenschnelle übertragen. SATA-SSDs benötigen dafür hingegen Minuten.
Videobearbeitung:
- NVMe-SSDs bieten höhere Lesegeschwindigkeiten, wodurch das Durchsuchen von 4K- und 8K-Videos flüssiger abläuft als mit SATA-SSDs. SATA-SSDs haben niedrigere Lesegeschwindigkeiten, was beim Durchsuchen großer Dateien zu Verzögerungen, Rucklern oder Verzögerungen führen kann.
Multitasking:
- NVMe ist ein Multitasker, da es mehrere Operationen gleichzeitig ausführt, ohne dabei langsamer zu werden.
Dieser Echtzeitvergleich zeigt, dass es bei NVMe SSDs nicht nur um hohe Zahlen geht, sondern auch um Ergebnisse im praktischen Einsatz.
NVMe SSD vs. SATA SSD: Welche sollten Sie wählen?
Wir haben NVMe vs. SSD und NVMe vs. SATA SSD besprochen, aber die Wahl des Produkts hängt von Ihren Bedürfnissen und Ihrem Budget ab.
- Eine SATA-SSD ist nur für Gelegenheitsnutzer geeignet, die lediglich im Internet surfen, streamen und Fotos speichern.
- Gamer und kreative Profis profitieren in vielerlei Hinsicht von einer NVMe-SSD.
- Personen mit älteren Geräten, die keine NVMe-Steckplätze unterstützen, haben nur die Möglichkeit, SATA-Anschlüsse zu nutzen.
Die Preise für NVMe-SSDs sinken stetig. Angesichts der Vorteile spielt der Kostenunterschied keine Rolle. Deshalb halten Technologieexperten NVMe nach wie vor für die klügere Wahl und eine lohnende Investition für die Zukunft.
Machen Sie Ihr System zukunftssicher mit einer NVMe-SSD
Mit zunehmender Größe von Software und Mediendateien wird der Speicherplatz knapp. Geschwindigkeit gewinnt an Bedeutung, da hochauflösende Videos, umfangreiche Spiele und KI-gestützte Anwendungen eine höhere Leistung erfordern.
NVMe-SSDs sind oft die beste Wahl, da sie dafür sorgen, dass Ihr System nicht so schnell veraltet wirkt. SATA-SSDs sind nach wie vor beliebt bei Nutzern mit älteren Systemen und begrenztem Budget. Der Trend zu NVMe ist jedoch deutlich erkennbar. Viele neue Laptops verzichten mittlerweile auf SATA.
Worauf Sie beim Kauf einer SSD achten sollten
Einige Punkte, die Sie beachten sollten, um Verwirrung beim Vergleich von NVMe- und SSD-Optionen bzw. NVMe- und SATA-SSD-Optionen zu vermeiden:
- Prüfen Sie die Kompatibilität, indem Sie herausfinden, ob Ihr Motherboard oder Laptop NVMe M.2-Steckplätze unterstützt.
- Welchen Formfaktor hat Ihr System? Desktop-Benutzer haben oft Platz für M.2 NVMe, bei Laptops kann dieser jedoch begrenzt sein.
- NVMe-SSDs können heiß werden; bei starker Beanspruchung sollten Kühlkörper oder externe Kühlung verwendet werden.
- Machen Sie sich mit dem Verhältnis von Speicherkapazität zu Budget vertraut, denn größere Festplatten sind zwar schneller, aber auch teurer.
- Wählen Sie NVMe für geschwindigkeitsintensive Anwendungen, SATA, wenn Sie nur einfachen Speicherplatz benötigen.
Abschluss
NVMe-SSDs und SATA-SSDs sind deutlich besser als herkömmliche Festplatten, aber im direkten Vergleich schneidet NVMe klar besser ab. Sie ist schneller und effizienter und eignet sich daher besser für moderne Anwendungen.
Für Gelegenheitsnutzer mit kleinem Budget ist eine SATA-SSD ausreichend. Wer jedoch Wert auf Geschwindigkeit, Zuverlässigkeit und zukunftssichere Leistung legt, sollte zu einer NVMe-SSD greifen.
Die beste Entscheidung ist, wenn Ihr System NVMe unterstützt, darauf zu setzen. Sie werden den Unterschied jeden Tag spüren.


Hinterlasse einen Kommentar
Diese Website ist durch hCaptcha geschützt und es gelten die allgemeinen Geschäftsbedingungen und Datenschutzbestimmungen von hCaptcha.